|
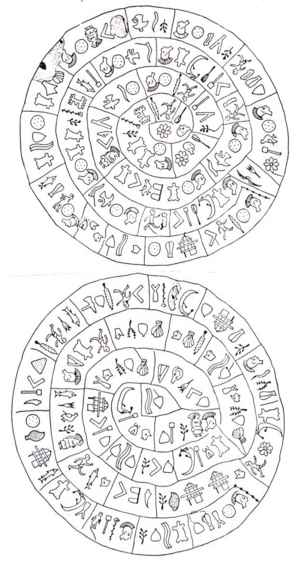
Clay disk which
found at 1908 under the ruins of the first palace of
Phaistos, considered to be constructed in the period
between 1700-1600 BC. It has a diameter of 17 cm and has
an inscription on it's both sides in an unknown
language, which has a spirally direction from the
circumference to the center.
The alphabet of
the disc consists of 241 independent and 61 common
signs, which seem to be a mixture of syllabic and
hieroglyphic writing. The elements had been stamped on
the disc with small seals before been cooked in ceramic
kiln.
 The
most frequent sign, is the appearance of a warrior head
with a cover which resembles the Philistine helmets.
Arthur Evans assumed that the script came from the Asia
Minor and probably from Lycia, and argued that the text
was an anthem in the honor of the goddess Cybele. The
most frequent sign, is the appearance of a warrior head
with a cover which resembles the Philistine helmets.
Arthur Evans assumed that the script came from the Asia
Minor and probably from Lycia, and argued that the text
was an anthem in the honor of the goddess Cybele.
Others believe
that the document regulated the transactions between the
rulers of Phaestos and the East. This is one of the most
famous works of art of the Minoan civilization, while
the enigmatic nature was the subject of intense interest
by many scholars, who occasionally made possible
proposals for the precise character of the disc.
|